*This post may contain affiliate links. This means we may make a commission if you purchase an item using one of our links*
White dwarfs have been observed continuously for multiple decades, from the matter that’s used to produce them, the speed at which they spin, how they’re made so on and so forth. In essence we actually know that they exist and aren’t just some fantasy thought up by some nut job.
The same can’t quite be said for black dwarfs. This is because the formation of a black dwarf isn’t set to happen for a theoretical quadrillion+ years. But, despite the lack of any physical evidence, the theory of black dwarfs eventually displaying its presence is a possibility.
White dwarf and black dwarf stars are in theory said to be the same size and mass but they are very different beyond this. White dwarf stars are said to burn at 100,000°C whilst black dwarfs are ice cold at -268°C. Black dwarfs are said to be virtually undetectable, incapable of going nova among many other points.
For a more in depth analysis on both dwarf stars from what they are, their similarities and differences and more, continue reading.
What Is A White Dwarf?
Table of Contents
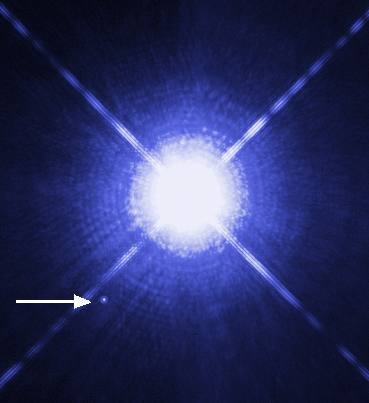
A white dwarf is a small star with an incredible density – while it is around the same size as a planet, its mass is more than 200,000 times that of Earth.
When a star forms, it gathers swirling clouds of dust and gas from its surrounding space to formulate a high-pressure core. The intense pressure creates nuclear reactions within this core that give off a terrific amount of light and heat.
However, the fuel that powers these stars is not unlimited, and one day the star’s finite resources run out. When a star runs out of hydrogen, it begins to conduct reactions with the helium outside of its core. As these reactions expand outwards, the star grows until gravity can no longer hold it together.
At this point, the outer material escapes from the star, leaving behind only the central nucleus, still burning brightly from the initial reactions. This core is known as a white dwarf and marks the final stage of the evolution of a star.
In essence, a white dwarf signifies that a star has run out of fuel and will now cool for a few billion years until it reaches the end of its life cycle.
What Is A Black Dwarf?

Black dwarfs are stars that have reached the end of their life cycle. This also means that the black dwarf status is what all white dwarf stars will theoretically become once they have run out of their energy resources.
In theory black dwarf stars are very small stellar remnants of stars, specifically white dwarfs, that achieve the end of their life cycle where they will emit insignificant heat or light, making them practically undetectable. The process itself is said to take an unimaginable amount of time to happen too.
According to astronomer Ethan Siegwl, it could take upwards of a quadrillion years for the first white dwarf to go dark therefore, even if black dwarfs are the theorised final stage of stellar remnants, it may never be something we truly uncover, unlike other interstellar bodies that we’ve already observed such as neutron stars or black holes.
As they’re essentially dead white dwarfs, black dwarfs would practically be the same size as them, projected to be roughly 5,000 to 10,000 km in diameter, and are likely to be as dense as white dwarfs. For reference an Earth sized black dwarf star would be roughly 200,000 times more dense than the Sun, practically invisible and undetectable due to the lack of light produced and ice cold at 5 degrees kelvin or -268 °C.
With that being said, this is what the theoretical black dwarf would look like so, until we legitimately observe one in the cosmos, we’ll never truly know if these celestial objects will actually match the figures our modern day astronomers have hypothesised.
Similarities Between White And Black Dwarf Star
Both stars do have their fair share of similarities, which would include the following:
- Both dwarf stars are extremely dense with an Earth sized variant of each star roughly 200,000 times the density of our Sun.
- The mass of both dwarf stars are the same if the same sized stars were to be compared.
- The gravitational effects on their surroundings are the same if the same sized stars are taken into account.
Differences Between White And Black Dwarf Stars
White dwarf stars are celestial entities formed when transforming from a red giant or other smaller stars nearing the end of their lifespan and only if they don’t explode is when black dwarf stars will form.
The differences stated here are purely speculation based on the theories of modern day astronomers so take them with a grain of salt but, the hypothesised differences would be as follows:
- Black Dwarf stars are said to have a temperature of 5 degrees kelvin or -268 °C whilst white dwarfs are said to burn at 100,000 °C.
- Black dwarfs are theorised to emit no light, making them barely detectable whilst white dwarfs can be detected even if they are around 1000 times less luminous than our Sun.
- It’s believed that white dwarfs will spin faster than black dwarfs meaning black dwarfs will have a weaker magnetic field.
- White dwarfs can go nova as a result the nuclear reactions that can be produced whilst black dwarfs will not have the required temperature for nuclear fusion to occur and potentially explode.
Summary
White dwarf stars are celestial entities we know a lot about, at least when compared to black dwarfs that theoretically cannot exists within our universe due to how long it would take them to form. All we can assume is that black dwarfs will simply be white dwarfs minus the heat, nuclear fusion and the ability to emit light that we can easily observe.

