*This post may contain affiliate links. This means we may make a commission if you purchase an item using one of our links*
The main differences between the Sun and Moon is that the Sun is the central entity in our solar system that all objects in its local region orbit, has a diameter of 1.39 million km and is the brightest entity in our solar system that produces energy for life to exist via nuclear fusion whilst the Moon is a gray rocky spherical natural satellite that orbits Earth.
There are numerous other differences between the Sun and Moon so, continue reading for a more in-depth look at each celestial objects, their similarities as well as there differences below.
What Is The Sun?
Table of Contents
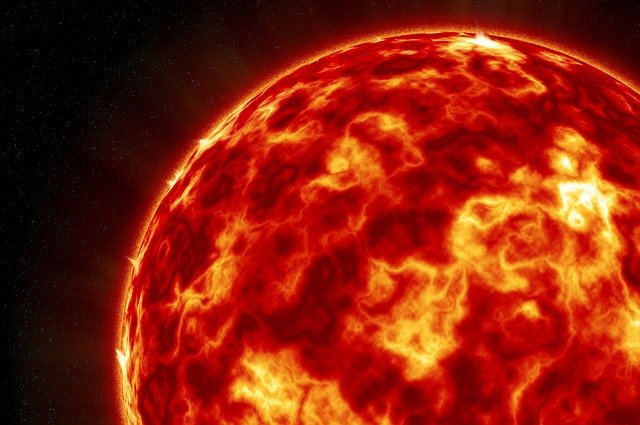
The Sun is the bright, celestial entity at the center of our solar system and is also a star that falls under the G type main sequence star bracket (also called a yellow dwarfs), all of which are medium sized stars that tend to be around 0.84 – 1.15 solar masses.
Our Sun is 1 solar mass, making it a medium sized medium star. It’s also on the brighter side for a yellow dwarf, the color that it emits is white as opposed to the slightly yellow that less luminous yellow dwarfs would be.
Of course we still see the Sun as yellow or even red on Earth but, the reason for this significant color shift is because our atmosphere scatters and breaks up the photons that reach us, ultimately changing the true color of the light rays from white to the yellow, orange or red we see in our day to day.
As it is a star, the Sun will actively convert the hydrogen elements at its core into helium, through a process called nuclear fusion.
Nuclear fusion is the reason why it generates light and produces the energy we receive, helping us power machinery, technology, grow crops so on and so forth.
The process of nuclear fusion also affects how hot our star burns, allowing the sun to hit temperatures around 6000°C on a daily basis. This will be the case for another 4.5 – 5 billion years until it’s unable to convert hydrogen into helium.
Once hydrogen cannot be converted, an imbalance between the inward and outward forces keeping the Sun together will occur, causing an imbalance which would result in our Sun bloating up many many times its current size.
When this happens it will enter its red giant phase, where it’ll be around 256 times larger than it is now.
This phase will last for around a billion years until it sheds it mass through a process called planetary nebula, leaving behind only a dead white dwarf remnant.
What Is The Moon?
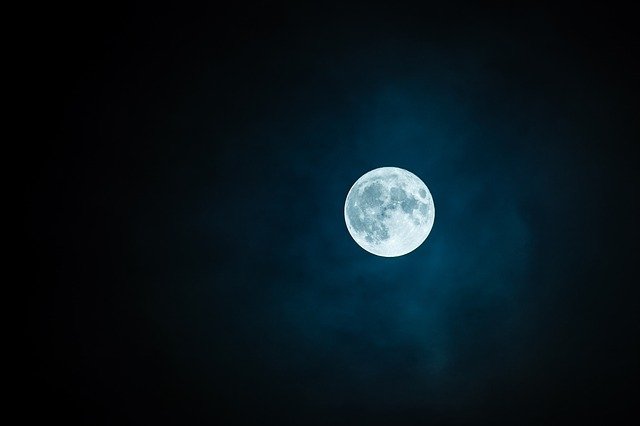

The moon is the gray celestial being that orbits our Earth. It is also tidally locked to Earth meaning that we only see one side of it at any time in our sky.
It takes the moon roughly 27 days to complete an orbit around Earth, which it does in an elliptical pattern. The Moon’s axial tilt is very straight at 1.5 degrees. As a result of the tidally locked status along with the effects that Earth has on its general rotational patterns, it takes the Moon roughly 29.5 days to complete a day.
In regards to its temperature, it fluctuates where it can be really hot at 127 degrees Celsius when the Sun is shining on it and to -173 degrees in areas where the Sun does not strike it. It’s core on the other hand is far hotter ranging between 1,327 to 1,427 degrees Celsius.
This is as a result of the lunar entity’s extremely thin to practically non-existent atmosphere, which not only results in these massive temperature shifts but, is also the reason why it has over 100,000 craters on its surface.
Speaking of the Moon’s surface, the entity is mostly made of rocks, iron, magnesium just like most of the other moons and terrestrial based planets in our solar system.
It is among the bigger moons in our solar system with a diameter of 3,474.8km and a mass of 7.35 × 10^22 kg, which actually places it fifth amongst all moons in our solar system and would also make it bigger than the dwarf planet Pluto.
Despite all the advancements in technology, the last time a manned mission was made to the Moon was on the Apollo 17 way back in December 1972 and no further missions have been done since, possibly as result of the political agendas behind the numerous countries vying for opportunities that we don’t know of.
Similarities Between The Sun And Moon
Although the Sun and Moon don’t have too many similarities, there still are a few features they do share, which in this case includes the following:
- Both are spherical in shape.
- Both have a hotter central core.
- Both are part of the same solar system.
Differences Between The Sun And Moon
As for the differences between the two, they include the below:
- The Moon is far smaller than the Sun with a diameter of 3,474.8km whilst the Sun has a diameter of 1.39 million km.
- As a result, the Sun has more mass than the Moon too where it is 1.989 × 10^30 kg or 1 solar mass whilst the Moon is 7.35 × 10^22 kg.
- The Sun’s magnetic field is significantly stronger than the Moon’s due to its size.
- The Moon is a terrestrial entity whilst the Sun is mostly gas based.
- The Sun is the hottest entity in our solar system where it has a temperature of 6,000 degrees Celsius whilst the Moon’s temperature fluctuates between 127 degrees Celsius and -173 degrees Celsius.
- In regards to the core temperature, the Sun’s is 15 million degrees whilst the Moon’s core temperature is 1,327 -1,427 degrees Celsius.
- The Moon orbits Earth in an elliptical pattern whilst the Sun does not orbit any other object.
- The Moon is tidally locked to Earth whilst the Sun is not tidally locked to anything.
- The Moon has no objects orbiting it whilst the Sun has the whole solar system orbiting it.
- The Sun goes through nuclear fusion whilst the Moon does not.
- When the Sun dies it will become a white dwarf whereas the Moon has no set day it will die to speak of.
Summary
The Sun and Moon are completely different entities. One is a giant ball of flames and energy in the center of the solar system whilst the other is a rocky natural satellite that orbits Earth.
The differences in size, temperature, effect on other entities and even composition show dissimilar they are to each other and is the reason why the fall under completely different brackets within the cosmos.

