*This post may contain affiliate links. This means we may make a commission if you purchase an item using one of our links*
Red dwarfs and red giants are both red stars that can be spotted in outerspace but, besides their similar color being and temperatures, around 2,200 – 3,200 degrees celsius, both stars are very different.
The main differences between the 2 are that red giants are 10000 times bigger than your average red dwarf, have masses that are around 0.3 – 8 solar masses as opposed to the sub 0.5 solar masses of red dwarfs, and that red dwarfs are active main sequence stars whilst red giants are on their last embers before dying.
For a more in depth breakdown of both stars as well as the similarities and differences between the two, continue reading.
What Is A Red Giant?
Table of Contents
A red giant is a star that is nearing the end of its lifespan, essentially entering the last stages of its evolution. The majority of stars in our Universe are known as main-sequence stars – or those which utilize nuclear fusion to convert hydrogen to helium.
During its ordinary life, the inward pressure of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure of nuclear fusion, which holds the mass together. But, when fusion ceases, the force of gravity exceeds the pressure of fusion, and the star begins to compress.
As this happens, it increases the temperature inside the star and ignites a burning hydrogen shell. The helium core continues to shrink while its temperature increases – and this gives energy to the hydrogen shell, which increases in luminosity as it continues to expand.
A red giant will grow 100 to 1000 times wider than the size of our sun, giving it a total width of somewhere between 100 million to 1 billion kilometers. And it’s this vast surface area that keeps the temperature relatively cool – 2,200 to 3,200 degrees celsius.
Our sun will turn into a red giant in around five billion years. At this point, the sun will engulf the inner planets as it expands.
Some stars can be bigger than your average red giants, such as a red supergiant, and even those that are amongst the brightest stars around called hypergiants. These are formed from dying stars are that far bigger in mass than the Sun and even those that fall under the supergiant moniker.
What Is A Red Dwarf?
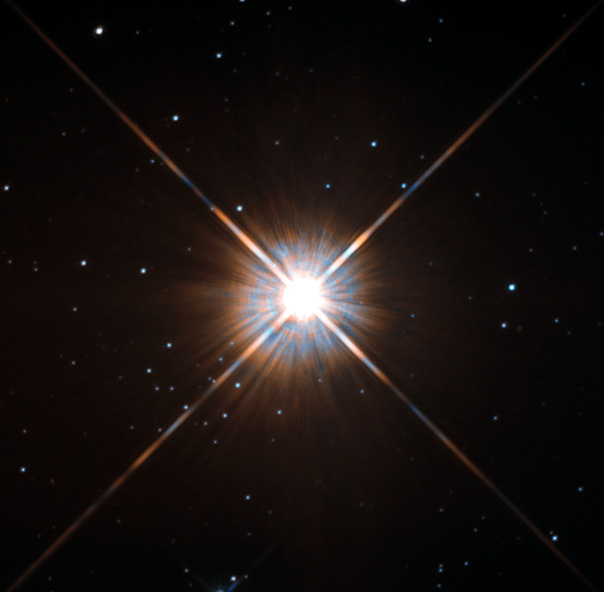

A Red dwarf is a star that possesses a very low mass, meaning they have low pressures, fusion rates, and temperatures. These factors mean that red dwarfs only glow with a dim light, making them difficult for astronomers to spot.
Some estimates suggest that up to three-quarters of the stars in our universe could be red dwarfs – yet none are visible to the naked eye.
While this type of star only emits 1/10,000 as much light as the sun, this is still a significant amount of light – around 10 trillion gigawatts. And this limited amount of radiance gives the red dwarf a considerable advantage – it extends its life far beyond that of a star such as our sun.
The definition of a red dwarf is vague, with no specific criteria for naming a star in this way. Instead, this label is given to many of the small, cool stars in a galaxy. These include K and M dwarfs.
A red dwarf forms in the same way as many other stars. Clouds of gas and dust swirl together under a gravitational force that allows them to group at the center. Once the central temperature is significant for fusion, this process begins, and a star is born.
Do Red Dwarfs Turn Into Red Giants?
Due to how long a red dwarf is theorised to live (upwards of 10 trillion years) as a consequence of their slower rate of nuclear fusion and how small they are, where a minimum solar mass of 0.25 is necessary for a theoretical red giant, It is highly unlikely that any red dwarf will go through a red giant phase.
In fact some have even theorised that our universe could come to end in the next 20 – 30 billion years, assuming a model of dark energy with w = −1.5 and the process of false vacuum decay occurring so, expecting a red dwarf to bloat up and become a red giant like yellow dwarfs and other bigger stars may not even happen within the lifespan of the universe itself.
Similarities Between Red Dwarfs And Red Giants
Both red dwarfs and red giants produce a red hue when they shine, which is because they are on the cooler end in regards to temperature. As for what their temperatures are, it’s estimated to be between 2,200 -3,300 degrees celsius. Both entities can create light too although, red giants are at the tail end of their existence as a living star.
Other than these points, both of these stars are very different from one another whether it be size, mass, their phases as a star, and so on.
Differences Between Red Dwarfs And Red Giants
As for the differences between the two, they include the following:
- Red dwarfs are by far the smaller of the 2 entities where they are will typically range between 0.08 – 0.5 solar masses in size whilst red giants can be anywhere from 0.3 – 8 solar masses.
- Red dwarfs are still actively converting hydrogen to helium through nuclear fusion in their whilst red giants are unable to convert hydrogen within their core as all of it has been converted.
- Red giants are more luminous than red dwarfs where they shine at only 0.0001 – 0.1 times that of the Sun whilst red giants can shine upto 1000 times the luminousity of the Sun. This is mostly down to the fact red giants are just that much bigger than red dwarfs.
- Red dwarfs are said to live for around an estimated 10 trillion years on the upper end of their lifespan whilst your average red giant, from a yellow dwarf like the Sun for example, will ‘only’ stick around for 1 billion years or so.
- When a red giant dies it will either do so through a supernova explosion resulting in either a neutron star or black hole or go through a planetary nebula phase, leaving behind a white dwarf. Red dwarfs on the other hand will become white dwarfs once at the end of their lifespan.
- Red dwarfs are the most abundant stars in the universe where they make up between 70 -75% of all stars in our universe. Red giants are few and far between in comparison.
- Red dwarfs are typically a few tenths the diameter of the Sun whilst red giants are anywhere from 100 – 1000+ times the size of the sun. In short, red giants really do live up to their namesake.
Summary
Although both are stars and red stars at that, in regards to size, luminosity, and lifespan, they differ significantly as oultined in the content above.
Red dwarfs are so abundant that they make up 70%+ of all stars in the universe but, they are among the weaker side for a star, in regards to magnetic field and power but, even at their smaller size, much like many other stars in the universe they will eventually cease to burn and become white dwarfs.

